Enterprise management software (EMS) is a suite of integrated applications designed to streamline and automate a wide range of business processes. These systems support functions such as human resources, financial management, supply chain management, customer relationship management, and more. By centralizing data and processes, EMS helps organizations improve efficiency, enhance decision-making, and ensure consistency across various departments. Data Bridge Market Research analyses that “the enterprise software market is expected to reach USD 450.68 billion by 2030.” Let’s get into the nuances of enterprise software management.
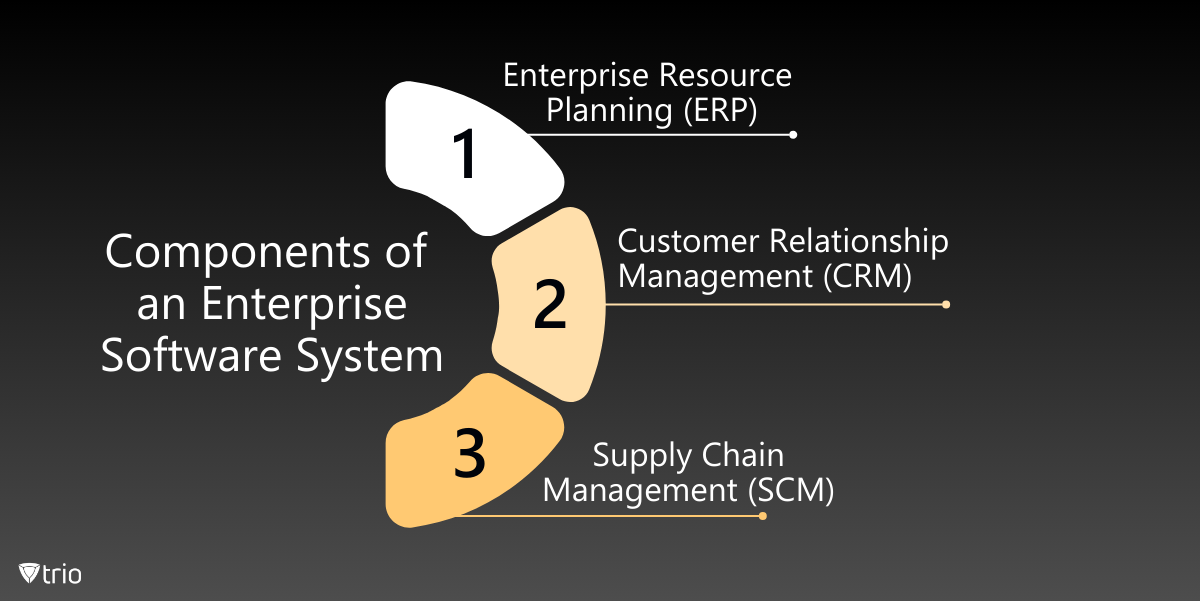
Components of an Enterprise Software System
An enterprise software system encompasses a variety of applications tailored to meet the needs of large organizations. These enterprise tools are robust, scalable, and capable of handling complex processes. Key components of enterprise software solutions typically include:
- Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP): Manages core business processes such as finance, HR, manufacturing, and supply chain.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Helps manage interactions with current and potential customers, improving customer service and sales.
- Supply Chain Management (SCM): Optimizes the flow of goods, information, and finances from suppliers to consumers.
These components are designed to work together, providing a comprehensive solution that enhances operational efficiency and supports strategic planning.
The Role of Enterprise Apps
An enterprise app is a software application designed to meet the needs of a large organization rather than individual users. These enterprise business software are complex, scalable, and typically integrate with other enterprise systems to facilitate various business processes and operations. Enterprise apps are used across different departments within an organization, such as human resources, finance, supply chain management, and customer relationship management, to improve efficiency, productivity, and data management.
Enterprise applications often require robust security features to protect sensitive business data and ensure compliance with industry regulations. They are built to handle large volumes of transactions and users, providing the necessary reliability and performance for mission-critical operations. Additionally, these applications often support multi-user environments and offer advanced functionalities like analytics, reporting, and automation to help organizations make informed decisions and streamline their workflows.
Examples of enterprise application platforms include Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems, Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software, Human Capital Management (HCM) systems, and Business Intelligence (BI) tools. These types of enterprise software can be deployed on-premises or hosted in the cloud, depending on the organization's needs and infrastructure. With the rise of digital transformation, enterprise apps are increasingly becoming cloud-based, enabling better scalability, flexibility, and accessibility for global workforces.
What does Enterprise Software Management have to do with Enterprise Mobility Management?
Enterprise Software Management (ESM) and Enterprise Mobility Management (EMM) are interrelated facets of organizational IT management, both aiming to enhance operational efficiency and security. ESM focuses on the administration, deployment, and maintenance of software applications across an organization. It ensures that all enterprise software is up-to-date, licensed correctly, and functioning optimally. This encompasses managing software assets, compliance with licensing agreements, and ensuring that software deployments are aligned with the organization's strategic goals.
EMM is concerned with managing and securing mobile devices, applications, and data in an enterprise environment. As organizations increasingly adopt mobile technologies, EMM’s benefits becomes critical in maintaining the security and productivity of mobile workforces. EMM solutions typically include mobile device management (MDM), mobile application management (MAM), and mobile content management (MCM), providing comprehensive control over mobile devices and ensuring that corporate data is secure, even on employees' personal devices.
The convergence of ESM and EMM is important in today’s digital workplace. Both domains require a seamless integration to ensure that enterprise applications are accessible and secure on mobile devices. This integration helps in maintaining compliance with security policies, ensuring that mobile applications receive timely updates, and protecting sensitive data across all devices. As mobile usage grows, the boundary between ESM and EMM blurs, necessitating a unified approach to manage both traditional and mobile software environments effectively.

Traditional Enterprise Software vs. SaaS
Enterprise software refers to applications designed to meet the needs of large organizations, supporting complex and scalable operations. These applications can be delivered through traditional on-premises installations or via cloud-based models like SaaS. The primary difference between traditional enterprise software and SaaS lies in deployment and maintenance.
Traditional enterprise software requires significant IT resources for installation, configuration, and ongoing management. This often involves substantial upfront costs and dedicated IT staff. In contrast, SaaS solutions are managed by the provider, offering lower initial costs, scalability, and ease of access from any location with internet connectivity. This shift to cloud-based solutions is driven by the need for greater flexibility and cost efficiency in software deployment.
Conclusion
Enterprise software management encompasses a broad range of applications and practices designed to support the complex needs of large organizations. From ERP and CRM to ETM and SaaS, these solutions provide the tools necessary for improving efficiency, enhancing decision-making, and achieving strategic goals. As businesses continue to evolve, the role of enterprise software in driving success becomes increasingly critical.
Enhance your organization's mobile device management with Trio, the leading solution designed to simplify the management of mobile devices across your enterprise. Ensure security, streamline processes, and boost productivity with Trio's comprehensive features. Try out Trio’s free demo today!
Get Ahead of the Curve
Every organization today needs a solution to automate time-consuming tasks and strengthen security.
Without the right tools, manual processes drain resources and leave gaps in protection. Trio MDM is designed to solve this problem, automating key tasks, boosting security, and ensuring compliance with ease.
Don't let inefficiencies hold you back. Learn how Trio MDM can revolutionize your IT operations or request a free trial today!





