Navigating the complex landscape of information technology requires a proactive and strategic approach to mitigate potential risks, including Smishing Attacks and Endpoint Detection and Response. From framing risk assessments to responding and monitoring, IT Risk Management or Information Technology Risk Management plays a pivotal role in ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT systems. In this blog post, we delve into the systematic process that organizations undertake to identify, assess, prioritize, and mitigate risks associated with the use of information technology. Read on to gain insights into the key components, benefits, and steps involved in safeguarding organizational assets in an ever-evolving digital environment.
What Is the IT Risk Management Process?
According to the U.S. Government’s Guide for Conducting Risk Assessments, “Risk management processes include framing risk; assessing risk; responding to risk; and monitoring risk.” Risk management in IT is a systematic process of identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and mitigating risks associated with the use of information technology (IT) within an organization.
The primary goal of IT Risk Management is to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of IT systems, data, and resources while supporting the organization's overall objectives. Key components of an IT Risk Management framework include:
- Risk Identification: Identifying potential risks and vulnerabilities associated with IT systems, infrastructure, and operations. This involves understanding the various threats that could impact the organization.
- Risk Assessment: Evaluating the likelihood and potential impact of identified risks. This step involves analyzing vulnerabilities, assessing their potential consequences, and determining the overall risk level.
- Risk Prioritization: Prioritizing risks based on their significance and potential impact on the organization. This helps in focusing resources and attention on addressing the most critical risks first.
- Risk Mitigation: Developing and implementing strategies to reduce or eliminate the identified risks. This may involve implementing security controls, adopting best practices, and taking corrective actions to enhance the security posture of IT systems.
IT risk management examples encompass a wide range of scenarios where organizations identify, assess, and mitigate risks associated with information technology. Here are some specific IT risk management examples:
- Data breach response plan
- Regular security audits and assessments
- Firewall implementation
- Encryption of sensitive data

Why Is IT Risk Management Important?
IT risk management is essential for safeguarding organizational assets, ensuring operational continuity, complying with regulations, and maintaining trust with stakeholders. It is a proactive approach that helps organizations navigate the complex and evolving landscape of IT threats and vulnerabilities. Let’s get into the details of each of these benefits of IT risk management:
Protection of Sensitive Information
Organizations often deal with sensitive and confidential information. IT risk management helps protect against company data breaches, ensuring the confidentiality of critical business and customer information.
Business Continuity
Identifying and mitigating potential risks ensures that IT systems remain operational and data loss is prevented. This is essential for business continuity, as disruptions to IT operations can lead to downtime, financial losses, and damage to an organization's reputation.
Prevention of Financial Loss
Cybersecurity threats and IT failures can result in significant financial losses. IT risk management aims to minimize the impact of such incidents, protecting an organization's financial assets and ensuring the cost-effectiveness of IT operations.
Maintaining Reputation and Trust
A security breach or data loss can damage an organization's reputation and erode customer trust. Effective IT security risk management helps prevent such incidents, contributing to the maintenance of a positive image and trust among stakeholders.
Strategic Decision-Making
Understanding and managing IT risks allow organizations to make informed and strategic decisions. By evaluating potential risks, leaders can make choices that align with the organization's risk tolerance and long-term objectives.
Adaptation to Changing Threat Landscape
The digital landscape is dynamic, with new threats emerging regularly. IT risk management ensures that organizations remain agile and adaptable, continuously monitoring and addressing evolving risks to prevent data breaches and other threats.
Efficient Resource Allocation
By prioritizing and addressing the most significant risks, organizations can allocate resources efficiently. This helps in optimizing investments in cybersecurity measures and ensuring that resources are directed toward the most critical areas of vulnerability. This also helps in disaster recovery, since effective resource allocation is important when an organization is facing the consequences of an incident.
Facilitating Innovation
An effective IT risk management framework provides a secure foundation for innovation. Organizations can confidently explore new technologies and business processes, knowing that potential risks are identified and managed.
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to IT risk management practices ensures that an organization complies with relevant laws and regulations. This is particularly important in industries where legal consequences for data breaches or security lapses are severe.

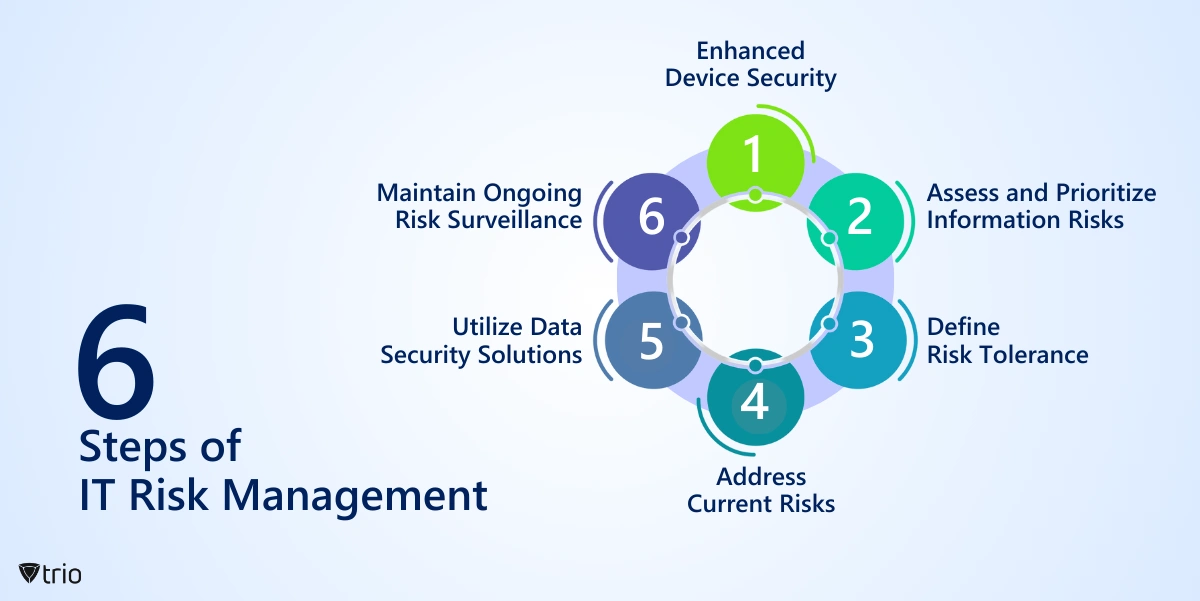
6 Steps of IT Risk Management
Though IT risk management is a complex process, it’s useful to break it down into steps. Here are six steps you should consider when going through the IT risk management process.
-
Examine Data Categories
Understanding the different types of data that an organization handles is crucial. This step involves categorizing and classifying data based on its sensitivity and importance. Not all data carries the same level of risk, so this analysis helps prioritize protection efforts. In this step, it’s also important to do vulnerability management, meaning realizing weak points that risk your organization.
-
Assess and Prioritize Information Risks
After identifying vulnerabilities and analyzing data types, organizations need to evaluate and prioritize the risks associated with potential threats. This involves assessing the likelihood of a threat occurring and the potential impact it could have on the organization's IT assets.
-
Define Risk Tolerance
Organizations need to define their risk tolerance, which is the acceptable level of risk they are willing to take. Once this is established, they can create and implement IT risk management processes and policies that align with their risk tolerance. This step sets the foundation for effective risk management.
-
Address Current Risks
With a clear understanding of current vulnerabilities and risks, organizations can develop and implement strategies to mitigate or reduce these risks. This may involve implementing security controls, enhancing employee training, updating software, or adopting other measures to minimize the likelihood and impact of potential threats.
-
Utilize Data Security Solutions
Implementing robust data security solutions is crucial for protecting sensitive information. This could include encryption, access controls, intrusion detection systems, and other technologies that help safeguard data from unauthorized access or manipulation.
-
Maintain Ongoing Risk Surveillance
IT risk management is an ongoing process. Continuous monitoring involves staying vigilant, regularly assessing the effectiveness of risk mitigation measures, and adapting strategies to address new and emerging threats. This step ensures that the organization's risk management practices remain relevant and effective over time.
Conclusion
Understanding and implementing IT Risk Management is indispensable for organizations seeking to thrive in the digital era, especially in the context of mobile security. Through IT Risk Management solutions, organizations can identify potential vulnerabilities and threats related to mobile devices, ensuring comprehensive protection of their digital assets. By breaking down the process into six actionable steps, we empower organizations to systematically navigate the complexities of IT risks, embrace ongoing surveillance, and fortify their digital foundations for sustained success. With a focus on mobile security, organizations can safeguard sensitive data and ensure the integrity of their IT infrastructure in an increasingly interconnected world.
MDM solutions play a pivotal role in mitigating risks associated with mobile devices within an organization. MDM solutions are different from IT risk management software. These solutions provide control and oversight over the use of smartphones, tablets, and other mobile devices, ensuring that they adhere to security policies and protocols. One such MDM solution is Trio. Try out Trio’s free demo and see how you can make a difference in mitigating and managing IT risks.
Get Ahead of the Curve
Every organization today needs a solution to automate time-consuming tasks and strengthen security.
Without the right tools, manual processes drain resources and leave gaps in protection. Trio MDM is designed to solve this problem, automating key tasks, boosting security, and ensuring compliance with ease.
Don't let inefficiencies hold you back. Learn how Trio MDM can revolutionize your IT operations or request a free trial today!





